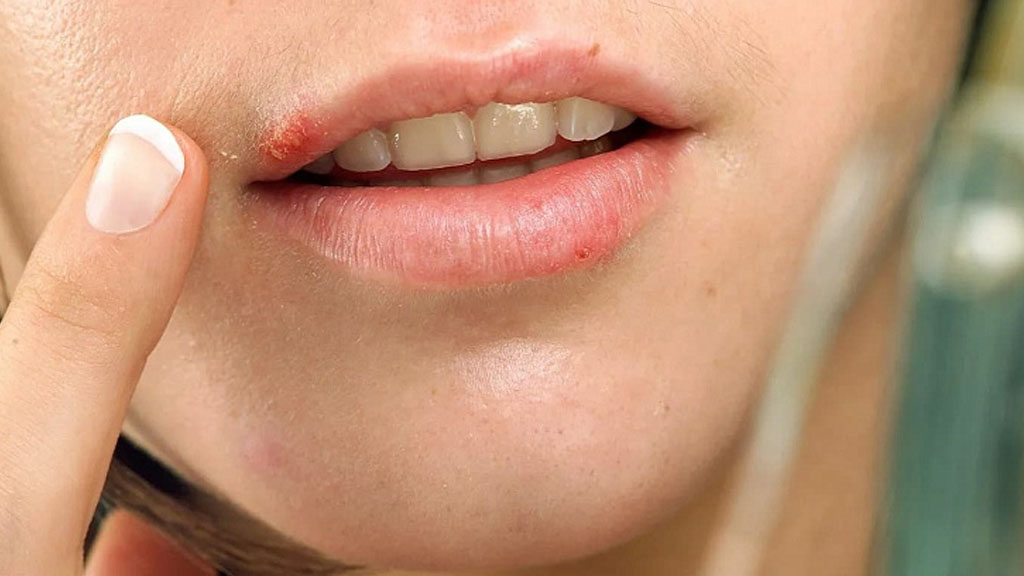
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV). It is highly contagious and can manifest in mild or severe forms. There are two main types of the virus:
- HSV-1 – commonly causes oral herpes (cold sores on the lips and mouth);
- HSV-2 – primarily responsible for genital herpes.
Symptoms of Herpes
Symptoms depend on the type of virus, the immune system’s strength, and the site of infection. In many cases, the first outbreak is the most intense, and the virus may remain dormant in the body, triggering flare-ups later.
Common symptoms include:
- Itching, tingling, or burning sensations before rash appears;
- Redness and swelling in the affected area;
- Small fluid-filled blisters;
- Pain or tenderness;
- Ulcers and crusts after blisters burst;
- Swollen lymph nodes, fever, and fatigue (especially during the first episode).
Oral Herpes (Cold Sores):
- Affects lips, mouth, nose area, or cheeks;
- Often begins with a tingling sensation;
- Lesions typically heal within 7–10 days.
Genital Herpes:
- Blisters around genitals, anus, or inner thighs;
- Pain during urination;
- Flu-like symptoms and body aches;
- May be asymptomatic, especially in men.
Triggers for Recurrence
After the initial infection, the virus remains dormant in nerve cells and can reactivate due to:
- Stress;
- Weakened immune system;
- Colds or flu;
- Hormonal changes;
- Exposure to cold or heat;
- Skin or mucosal damage.
Treatment for Herpes
There is no cure for herpes, but symptoms can be managed and recurrence minimized.
Main treatment options:
1. Antiviral Medications:
- Acyclovir (Zovirax) – cream or oral;
- Valacyclovir (Valtrex) – oral;
- Famciclovir (Famvir) – oral.
These drugs help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, especially if taken within the first 24–48 hours of onset.
2. Topical Treatments:
- Antiviral creams (e.g., Acyclovir);
- Pain-relieving gels;
- Protective lip balms.
3. Immune Support:
- Recommended for frequent outbreaks;
- May include vitamins, interferons, or herbal immune boosters (e.g., echinacea, eleuthero).
4. Natural Remedies (supportive use only):
- Tea tree oil or aloe vera on sores;
- Chamomile or calendula compresses;
- Honey or propolis (use with caution).
⚠️ Important: Self-treatment may be risky. If symptoms are severe, recurring, or involve the genital area — consult a healthcare provider.
Prevention Tips
- Avoid direct contact with active sores;
- Use personal hygiene items only;
- Don’t touch sores and avoid touching your eyes or other sensitive areas;
- Boost your immune system with a healthy lifestyle;
- Use condoms and avoid sexual activity during outbreaks (for genital herpes).
Final Thoughts
Herpes is more than just a “cold sore.” It can be a sign of lowered immunity and may cause significant discomfort. While there is no cure, modern medicine offers effective ways to manage it. Early treatment and prevention are key to controlling symptoms and reducing transmission.